Billionaire CEO of SpaceX launches satellite into orbit and promises to provide a high-speed broadband internet connection to as many users as the satellite internet Starlink company
When you think of billionaire businessman Elon Musk, chances are you think it's his electric car company, Tesla.
SpaceX's space-area exploits or recent work as a Saturday Night Live presenter (not to explain anything about its history that raised the pros and cons on social media).
or smoking marijuana with Joe Rogan). Chances are you just recognized him as one of the richest people on Earth.
Something you may not recognize is Musk's efforts mentioned by Starlink,
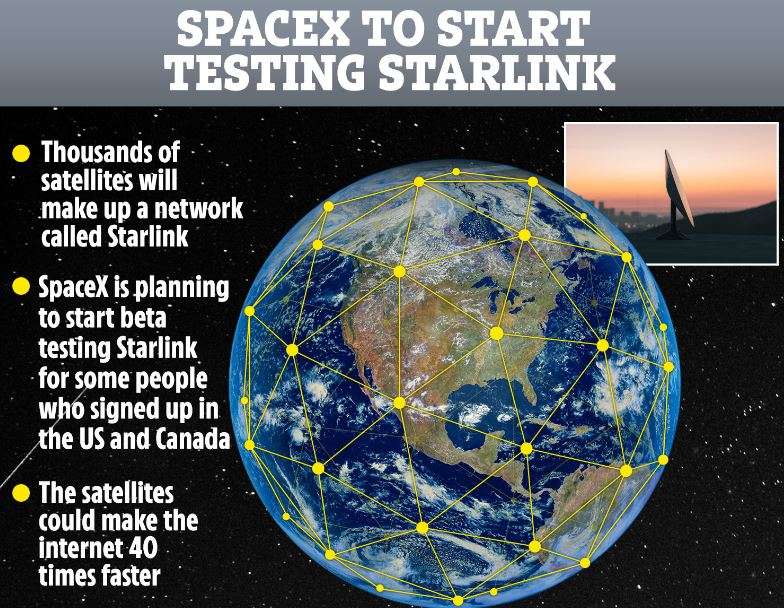
StarLink internet satellites have the goal to sell internet access to almost everyone on the planet through a growing network of private satellites orbiting overhead.
After years of improvements in SpaceX — and after getting nearly $885.5 million in grants from the Federation Communications Commission by the end of 2020 — Starlink's development appears to be accelerating in 2021.
In January, after about 3 years of successful smuggling,
The satellite's Starlink internet project exceeds the 1,000 satellites delivered into orbit — currently, in June, SpaceX explained the number of about 1,800. In February, Musk's company said Starlink serves more than 10,000 loyal customers.
This service is in the process of extending preorders to a growing number of prospective loyal consumers,
Some people who are currently living without a connection to high-speed internet as one of the main focuses.
Table of Contents
What exactly is Starlink?
Technically a subsidiary of SpaceX, Starlink internet satellites is the name of a network of space flight companies that develop – or “shape” – orbital satellites. The network upgrade began in 2015, with the first archetype satellite ejected into orbit in 2018.
In the years since SpaceX has deployed more than 1,000 Starlink internet satellites into orbit in dozens of successful launches.
In January, for the first-time Starlink vision in 2021, SpaceX passed 60 satellites into orbit from the new year.
Kennedy Space Center uses a Falcon 9 orbital rocket that can be re-rejected.
The latest launch, which recently sent 60 satellites back into orbit on May 26,
has brought the total number of satellites in the form up to 1,737,
Although some of the satellites are archetypes or non-operational units that are not functional sides. from the network.
Same with existing satellite internet suppliers such as
HughesNet or Viasat, Starlink wants to sell internet connection – especially to some people in rural areas,
and the other side of the world that does not have high-speed broadband access.
Starlink Internet Satellite package spacex hardware
SpaceX's Satellite Internet Starlink hardware includes a parabola and router,
You will prepare in the house to receive signals in space.
“Starlink is perfect for a place in the world where the connection is generally an obstacle,” notes Starlink's website. “Not limited by traditional land infrastructure, Starlink could provide it with high-speed broadband internet to the
locations where access cannot be handled or completely unavailable.”
The important thing you do to make a network is to prepare a small parabola in your home to receive signals and continue bandwidth to your router.
There's even a Starlink program for Android and iOS that uses augmented reality to help loyal consumers choose the best location and status for their receivers.
Satellite internet Starlink services only exist in certain areas of the U.S., Canada, and abroad at this time,
but this service currently offers more than 10,000 loyal consumers,
and the map of achievements will continue to increase along with more and more satellites coming into shape.
Ultimately, Starlink hopes to envelop all the planets in a high-speed Wi-Fi signal that can be used.
How fast is Starlink internet service?
“Users can want to watch the data speeds vary,
from 50 to 150 megabits per second and latency from 20 to 40 milliseconds in the majority of locations throughout some time ahead,” Starlink's website says.
It reminds me of a short time with no connection at all.
“As we take out more and more satellites, pair more and more ground stations and upgrade our network software,
Data speed, latency, and uptime will increase dramatically.”
How much does Starlink cost?
Starlink satellite internet has started to receive preorders from loyal consumers who are interested in joining the company's “Better Than Nothing” beta program.
Service fees are charged at $99/month, added taxes and fees, added an initial payment of $500 for the built-in parabolas and routers that you need to install at home.
Where is Starlink?
For now, Starlink internet satellite service is limited to the northwest U.S., the Canadian side that is side by side, some of the United Kingdom,
and certain other places, but the scope map will grow rapidly as more and more satellites are joined by shapes.
Starlink's internet satellite opportunity will require a minimum of 10,000 satellites in orbit before it can claim full service to the majority of the world (and SpaceX has shown signs that it wants about 30,000 satellites in shape). Today, only about 20% of the journey there, with a scope centered on areas that are between 45 and 53 degrees north latitude.
However, Musk still remains confident about the Starlink timeline.
Throughout the interview at Mobile World Congress 2021, Musk explained that Starlink will be around the world except in the Arctic and South from August.
Initially, in June, SpaceX president Gwynne Shotwell shared the same sentiment, explaining that Starlink would achieve global service waivers this fall.
Why satellites, sich? Can’t fiber be faster?
Fiber, or internet-delivered over ground-mounted fiber optic cables, promises faster upload and download speeds than satellite internet — but,
As will be mentioned by companies like Google,
No one is quick in applying the infrastructure needed to obtain fiber. To some people's homes.
That doesn't mean there's something simple about shooting a satellite into space,
But with fewer sharp competitors — and fewer bureaucracies that need to go through — there are some arguments for believing that services like Starlink will reach the majority of underserved people. People long before fiber ever existed. Recent FCC filings show that satellite internet could eventually double as a special telephone service as well.
What about bad weather and other obstacles?
That's certainly one of the shortcomings of satellite internet.
Per the Starlink FAQ satellite internet, which accepts the 100th snow landing on it, but can't do anything about the snow packing around it and other obstacles might block its vision to the satellite.
“We reference pairing Starlink in locations that avoid snow piling and other barriers hindering the viewing sector,” reads the FAQ. “Heavy rain or wind can affect your satellite's internet access, potentially resulting in slower speeds or infrequent outages.”